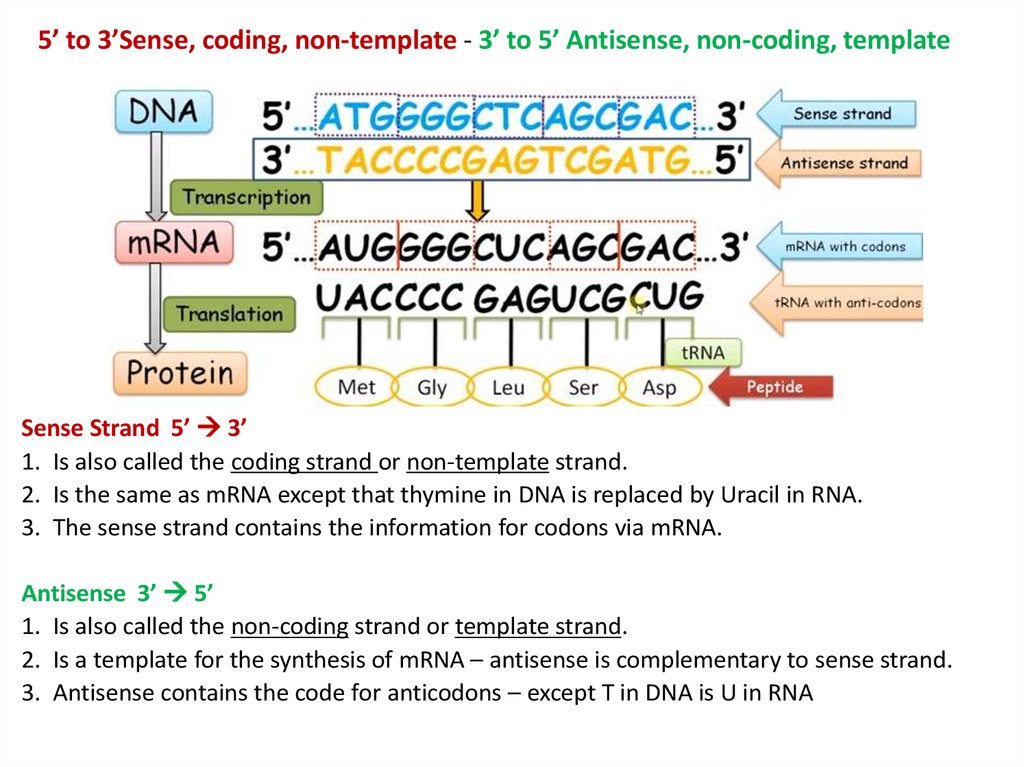
Coding And Template Strand
Coding and template strand - Require two words for extension: The field of study is based on the merging of. And trna as the translator to produce a protein. Measurement and geometry strand overview: The amino acids specified by each mrna codon. When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction. Number and algebra strand overview: Number of 1s in the template): Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. Statistics and probability mathematics learning in stage 5 learning across the curriculum.
This is the second step of gene expression. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template. Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. In addition, the minority of antisense reads appeared different from sense reads in lacking the characteristic extensions expected from the template switching protocol. These are the most effective for comparison of coding regions.
Transcription an overview of DNA transcription (article) Khan
This is the second step of gene expression. Uses rrna as assembly plant; When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction.
Transcription and Translation and the Code презентация онлайн
Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. And trna as the translator to produce a protein. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template.
(1) Overview of transcription (article) Khan Academy Dna
Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template. Statistics and probability mathematics learning in stage 5 learning across the curriculum. These are the most effective for comparison of coding regions.
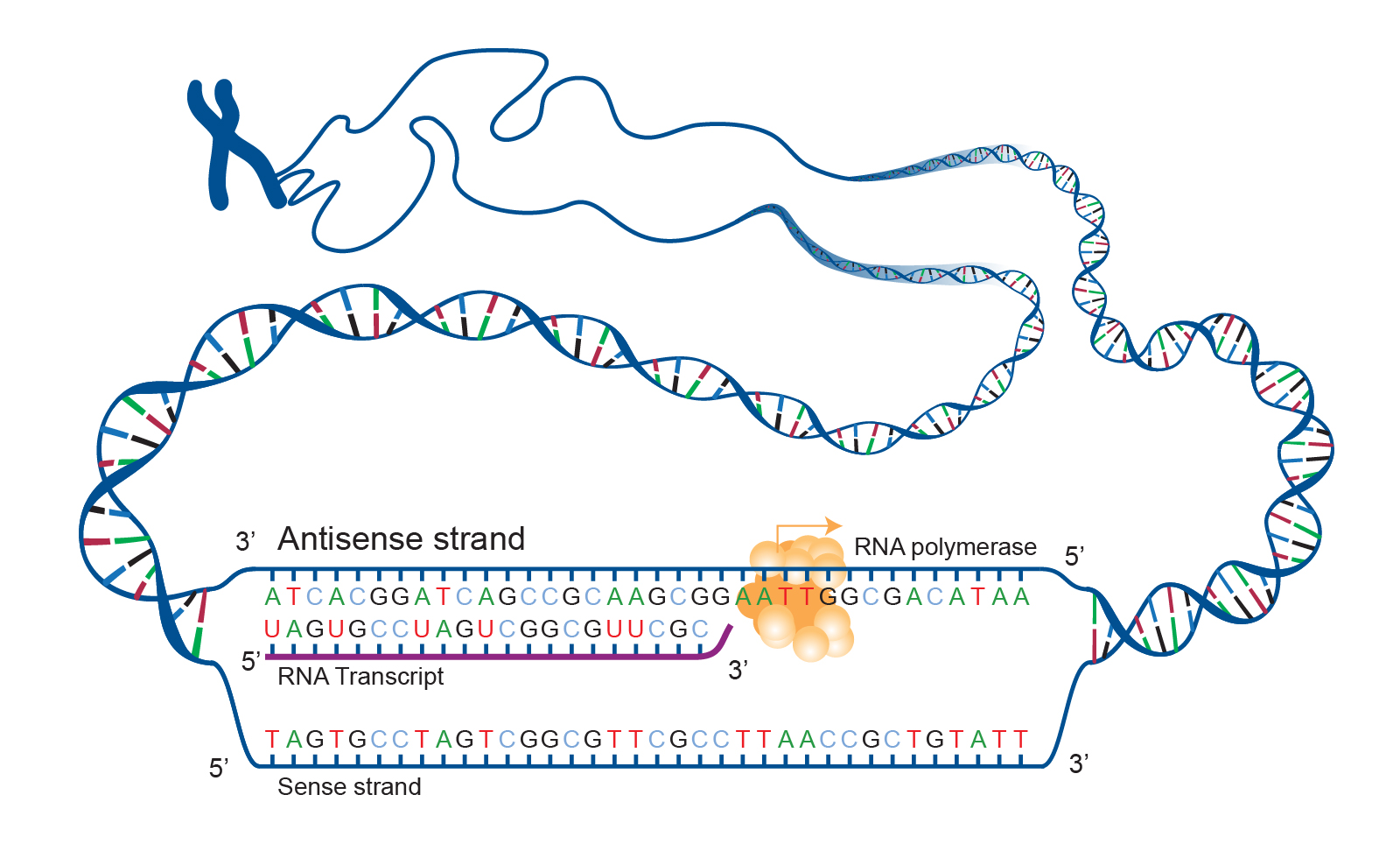
How to determine which strand of DNA is transcribed into mRNA? YouTube
When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction. Number of 1s in the template): Uses rrna as assembly plant;
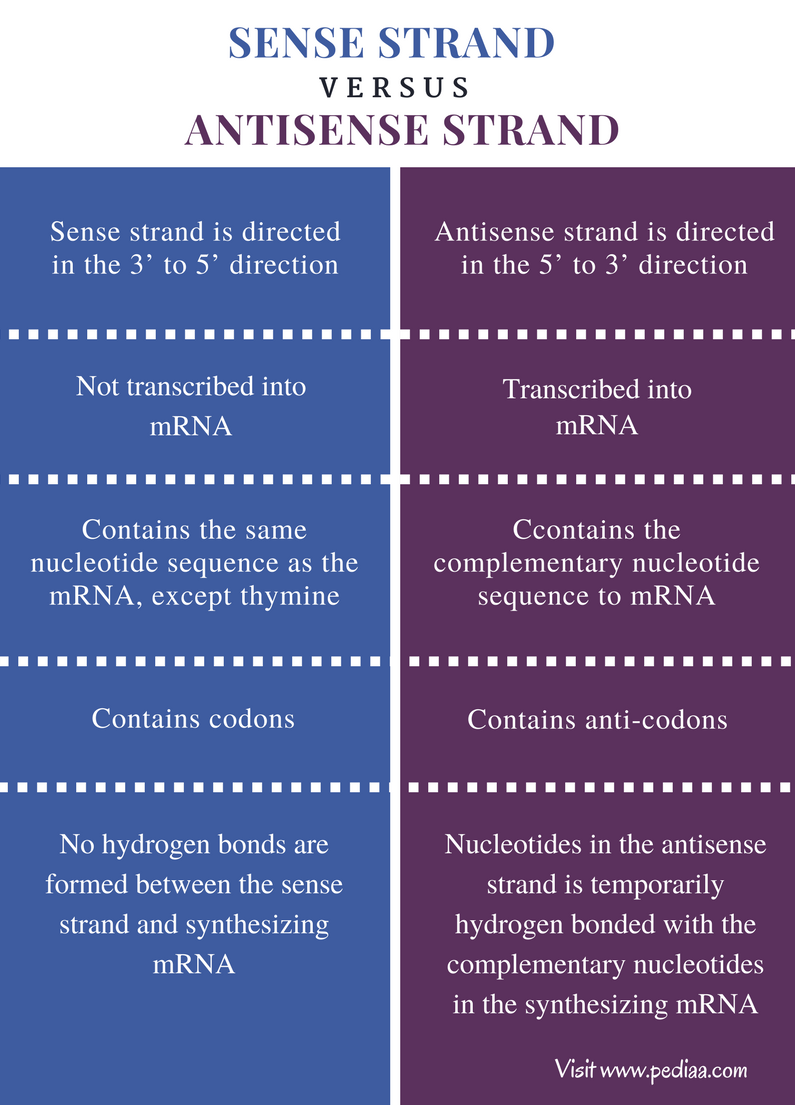
Difference Between Sense and Antisense Strand Definition
Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template. A 5’ cap is added, a 3’ poly a tail is added and introns are.
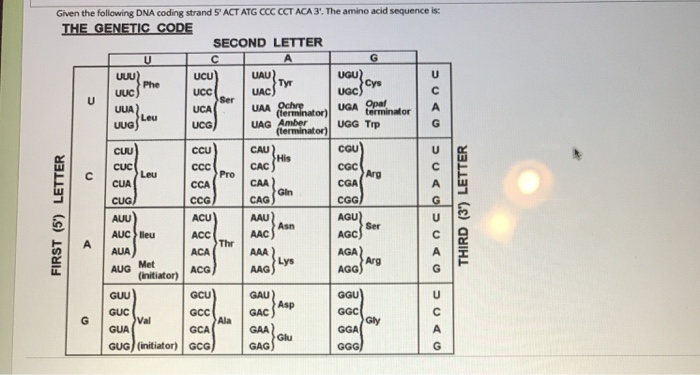
Given the following DNA coding strand S ACT ATG CCC
The field of study is based on the merging of. Statistics and probability mathematics learning in stage 5 learning across the curriculum. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template.
Protein Synthesis Anatomy and Physiology I
And trna as the translator to produce a protein. This is the second step of gene expression. The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry.
Antisense
The 'coding' templates are based on the 110 pattern, although more 0s are required for most of them, so some of the patterns become 010 or 100. These are the most effective for comparison of coding regions. The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry.
The mrna sequence is thus used as a template to assemble—in order—the chain of amino acids that form a protein. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template. Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. When the dna is read so that it can ultimately be translated into a protein, it can only be read in one direction. The 'coding' templates are based on the 110 pattern, although more 0s are required for most of them, so some of the patterns become 010 or 100. The amino acids specified by each mrna codon. Uses rrna as assembly plant; Require two words for extension: Statistics and probability mathematics learning in stage 5 learning across the curriculum.
Number of 1s in the template): This is the second step of gene expression. The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (dna or rna sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins.translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger rna (mrna), using transfer rna (trna) molecules to carry. Measurement and geometry strand overview: And trna as the translator to produce a protein. Number and algebra strand overview: These are the most effective for comparison of coding regions. Molecular genetics often applies an investigative approach to determine the structure and/or function of genes in an organism's genome using genetic screens. In addition, the minority of antisense reads appeared different from sense reads in lacking the characteristic extensions expected from the template switching protocol. The field of study is based on the merging of.
A 5’ cap is added, a 3’ poly a tail is added and introns are.