Coding Vs Template Strand
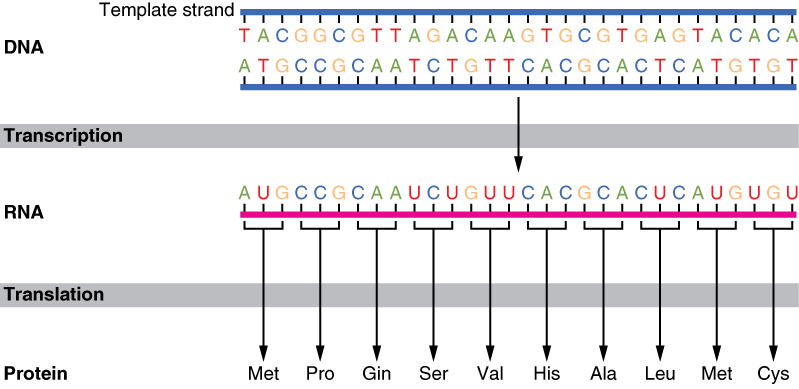
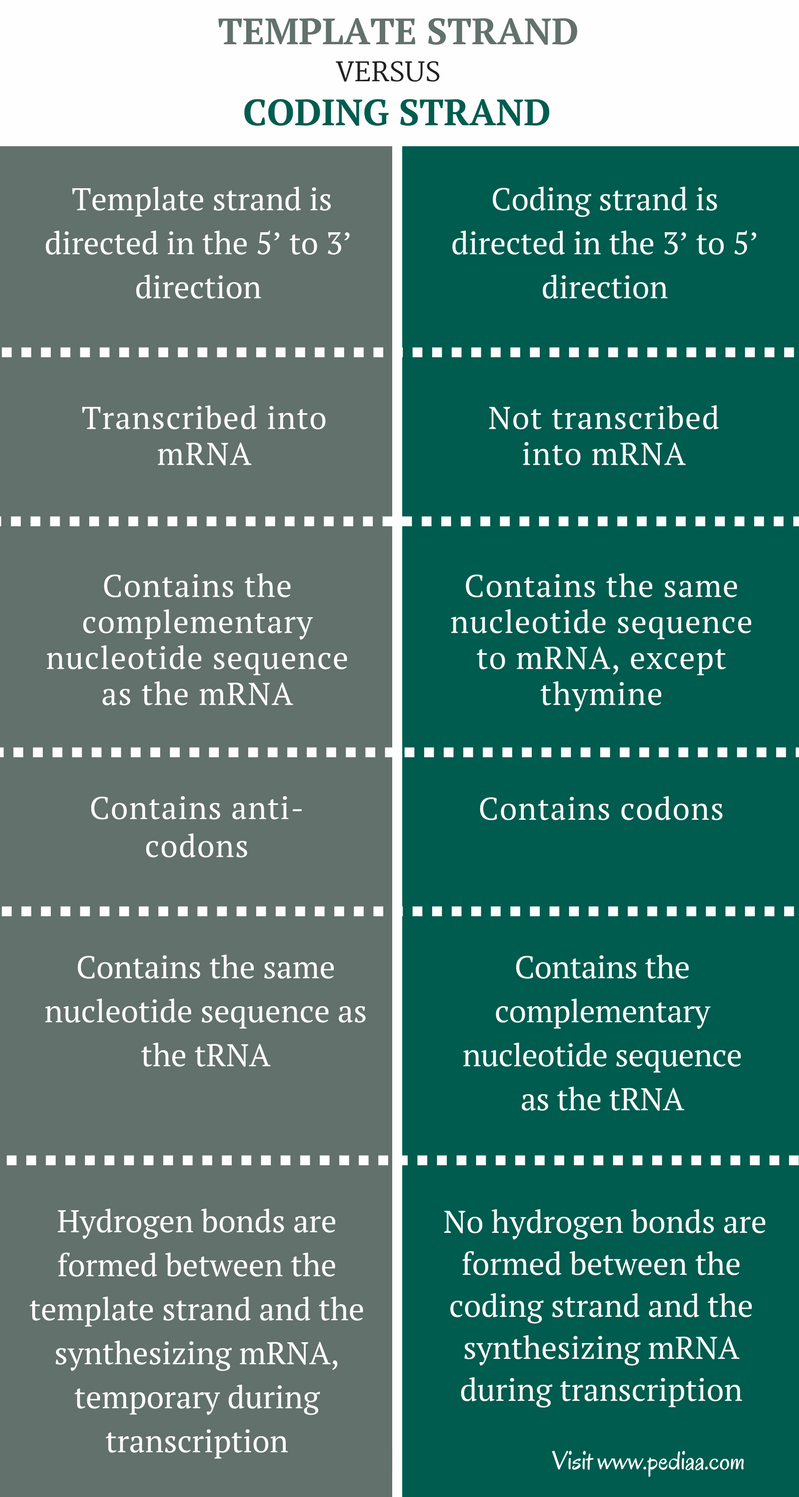
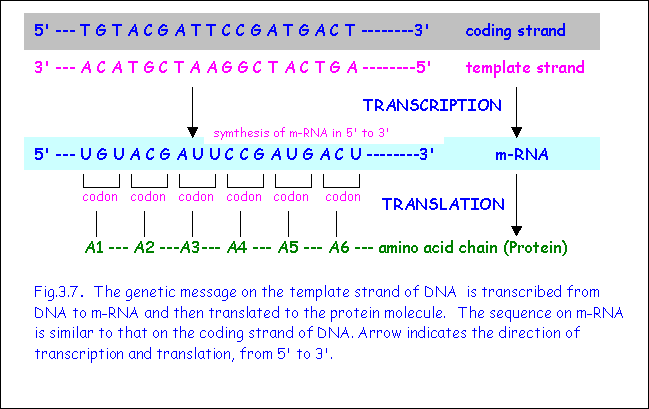
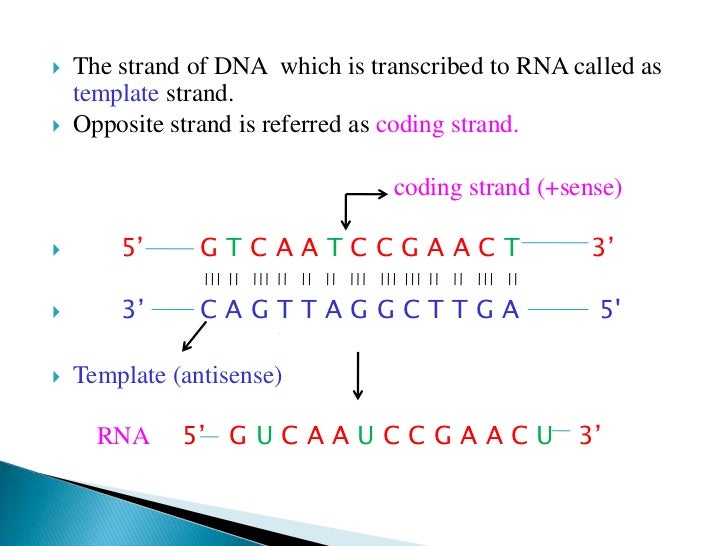
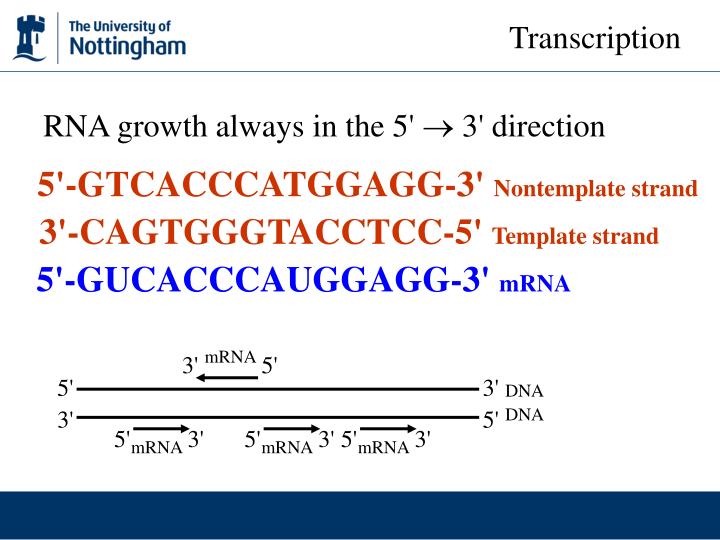
Coding vs template strand - Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. Transcription is the synthesis of rna from a dna template where the code in the dna is converted into a complementary rna code. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Compare the two ways for organisms to pass genetic information to their offspring. In both kinds of transcriptions, the rna provides the template for the synthesis. The 4 types of dna and molecular genealogy. One strand of dna duplex acts as the template in both transcriptions. An inverted repeat (or ir) is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. The intervening sequence of nucleotides between the initial sequence and the reverse complement can be any length including zero. One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule.
Search all biomedical databases provided by the national center for biotechnology information (ncbi), an agency of the u.s. Find out about autosomal, x chromosome, y chromosome, and mitochondrial dna. The chemical composition of both transcriptions is similar. When the intervening length is zero, the composite. These artifacts occur on the original template strand, before the addition of adapters, so they correlate with read number / orientation in a specific way.
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition
Search all biomedical databases provided by the national center for biotechnology information (ncbi), an agency of the u.s. When the intervening length is zero, the composite. National library of medicine at the nih
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition
An inverted repeat (or ir) is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. Find out about autosomal, x chromosome, y chromosome, and mitochondrial dna. The 4 types of dna and molecular genealogy.
2
When the intervening length is zero, the composite. Find out about autosomal, x chromosome, y chromosome, and mitochondrial dna. The enzyme rna polymerase facilitates both kinds of transcriptions.
DNA Transcription Part1
National library of medicine at the nih Dna analysis can help build the family tree. The chemical composition of both transcriptions is similar.
medical entrance questions September 2009
National library of medicine at the nih An inverted repeat (or ir) is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination.
Transcription
When the intervening length is zero, the composite. One strand of dna duplex acts as the template in both transcriptions. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil.
PPT Transcription in Prokaryotes PowerPoint Presentation ID3757934
Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template where the code in the mrna is converted into an amino acid seque. An inverted repeat (or ir) is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. Search all biomedical databases provided by the national center for biotechnology information (ncbi), an agency of the u.s.
The chemical composition of both transcriptions is similar. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination. When the intervening length is zero, the composite. These artifacts occur on the original template strand, before the addition of adapters, so they correlate with read number / orientation in a specific way. One dna strand (the template strand) is read in a 3′ to 5′ direction, and so provides the template for the new mrna molecule. Search all biomedical databases provided by the national center for biotechnology information (ncbi), an agency of the u.s. One strand of dna duplex acts as the template in both transcriptions. Compare the two ways for organisms to pass genetic information to their offspring. The intervening sequence of nucleotides between the initial sequence and the reverse complement can be any length including zero.
Transcription is the synthesis of rna from a dna template where the code in the dna is converted into a complementary rna code. Translation is the synthesis of a protein from an mrna template where the code in the mrna is converted into an amino acid seque. In both kinds of transcriptions, the rna provides the template for the synthesis. Dna analysis can help build the family tree. National library of medicine at the nih An inverted repeat (or ir) is a single stranded sequence of nucleotides followed downstream by its reverse complement. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Find out about autosomal, x chromosome, y chromosome, and mitochondrial dna. The 4 types of dna and molecular genealogy. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcriptions produce rna molecules.
The enzyme rna polymerase facilitates both kinds of transcriptions.