Dna Polymerase Reads The Dna Template Strand From The
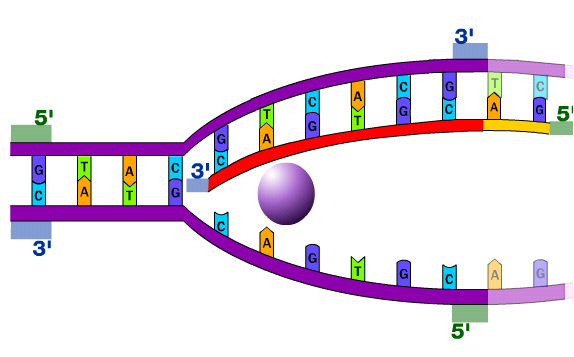
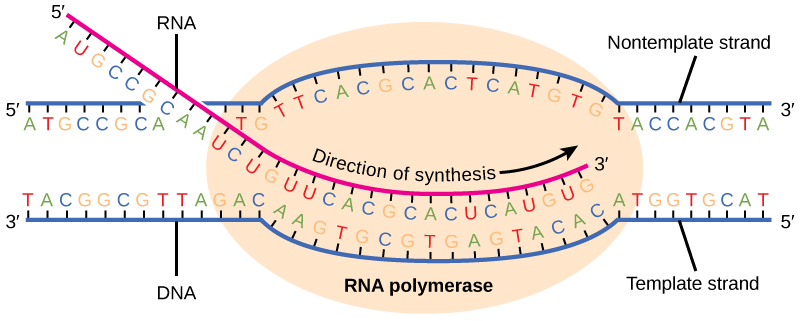
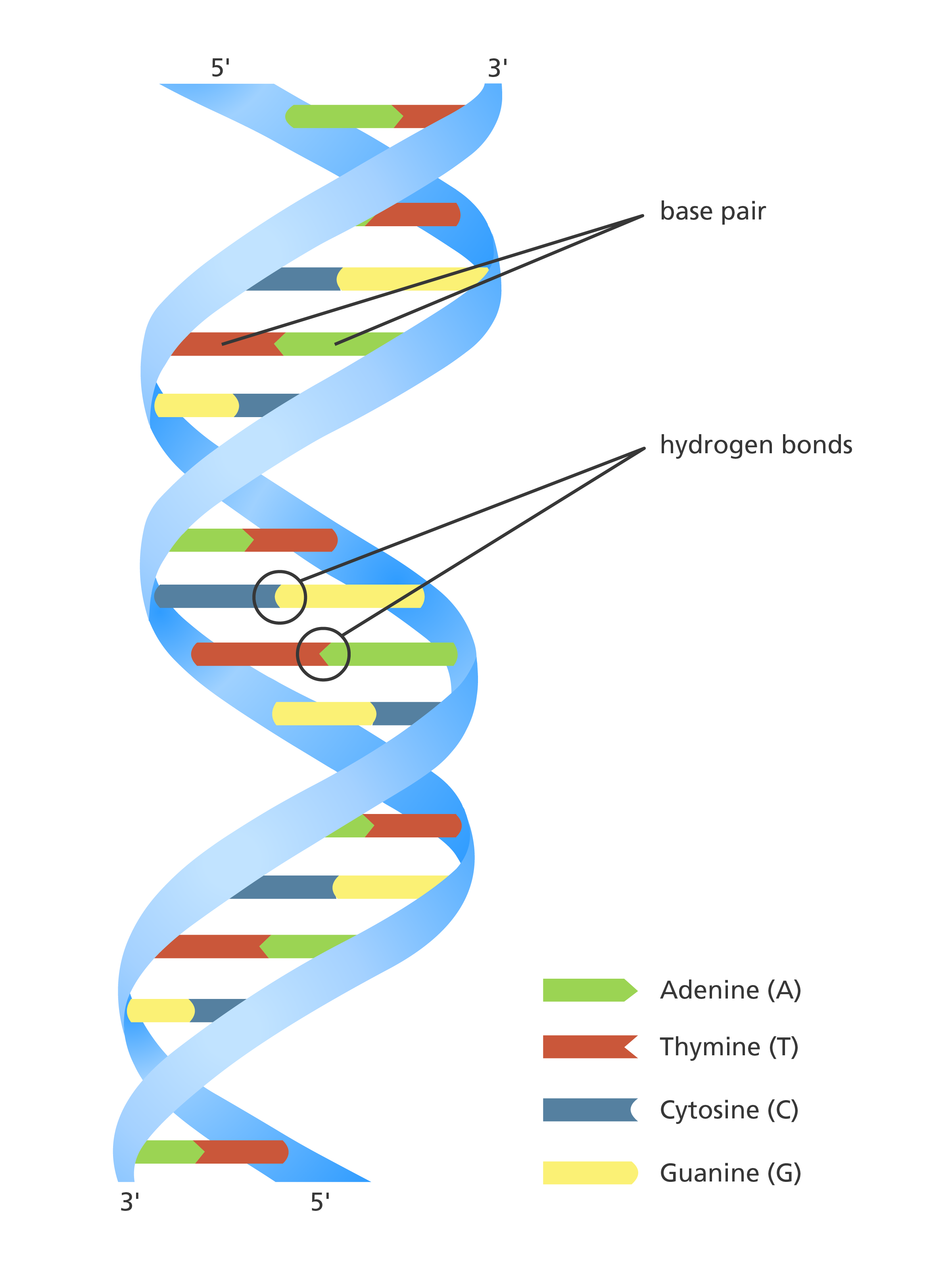
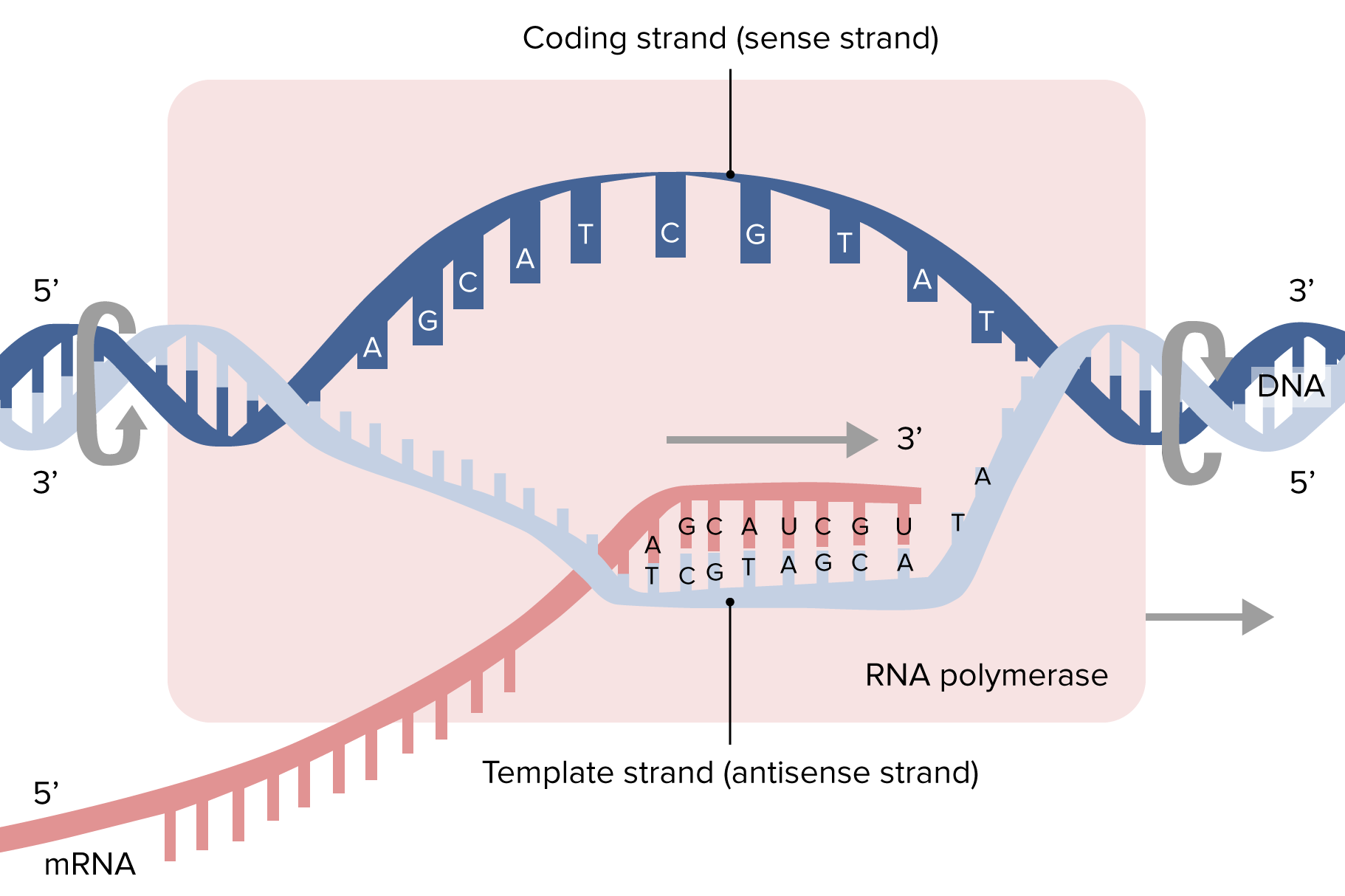
Dna polymerase reads the dna template strand from the - The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. If it detects a mismatch, it can ‘snip out’ the wrong nucleotide and replace it with the right one. To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna. It is important that dna polymerase accurately copies the template strand to avoid placing the wrong dna nucleotide in the incorrect position. Hence, this enzyme reads the just added nucleotides, and if there is any mismatch with the template strand, it will be removed. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity.
Molecular Biology DNA Replication Quiz! ProProfs Quiz
It is important that dna polymerase accurately copies the template strand to avoid placing the wrong dna nucleotide in the incorrect position. If it detects a mismatch, it can ‘snip out’ the wrong nucleotide and replace it with the right one. To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna.
9.3 Transcription Concepts of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
If it detects a mismatch, it can ‘snip out’ the wrong nucleotide and replace it with the right one. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. It is important that dna polymerase accurately copies the template strand to avoid placing the wrong dna nucleotide in the incorrect position.
The lagging strand of DNA is synthesized discontinuouslyduring
Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity. The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna.
Molecular diagnostics in hematopathology Rodak's Hematology Clinical
The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity. To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna.
Distinct energetics and closing pathways for DNA polymerase β with 8
It is important that dna polymerase accurately copies the template strand to avoid placing the wrong dna nucleotide in the incorrect position. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna.
Can essential oils repair DNA? (the short answer is "no") Tisserand
To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna. The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity.
Stages of Transcription Concise Medical Knowledge
Hence, this enzyme reads the just added nucleotides, and if there is any mismatch with the template strand, it will be removed. The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. If it detects a mismatch, it can ‘snip out’ the wrong nucleotide and replace it with the right one.
Protein Synthesis ‹ OpenCurriculum
Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity. The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. If it detects a mismatch, it can ‘snip out’ the wrong nucleotide and replace it with the right one.
The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. Hence, this enzyme reads the just added nucleotides, and if there is any mismatch with the template strand, it will be removed. If it detects a mismatch, it can ‘snip out’ the wrong nucleotide and replace it with the right one. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. It is important that dna polymerase accurately copies the template strand to avoid placing the wrong dna nucleotide in the incorrect position. Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity. To avoid this, dna polymerase ‘proofreads’ the complementary strand as it moves along the dna.