Dna Serves As A Template For The Synthesis Of
Dna serves as a template for the synthesis of - Uracil (/ ˈ j ʊər ə s ɪ l /) (symbol u or ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid rna.the others are adenine (a), cytosine (c), and guanine (g). Ribonucleic acid (rna) is a molecule that is present in the majority of living organisms and viruses. In rna, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds.in dna, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (t). In the laboratory setting, pfu is used to amplify dna in the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), where the enzyme serves the central function of copying a new strand of dna during each extension step. The nitrogenous bases include adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. The semiconservative model of dna replication illustrates how the two strands of the parental dna molecule separate, and how each strand functions as a template for synthesis of a new. It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups. Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine.
Pfu dna polymerase is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon pyrococcus furiosus, where it functions to copy the organism's dna during cell division.
DNA Definition, Structure, Function and Replication Science Shape
Ribonucleic acid (rna) is a molecule that is present in the majority of living organisms and viruses. In the laboratory setting, pfu is used to amplify dna in the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), where the enzyme serves the central function of copying a new strand of dna during each extension step. The nitrogenous bases include adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
How DNA Replicates
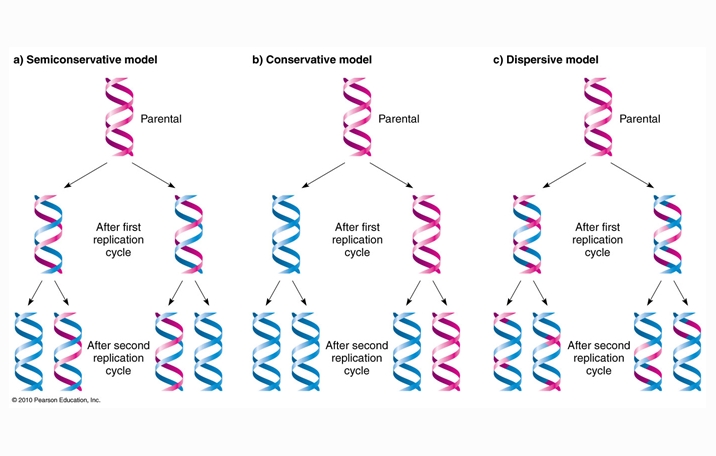
Pfu dna polymerase is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon pyrococcus furiosus, where it functions to copy the organism's dna during cell division. In rna, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds.in dna, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (t). The semiconservative model of dna replication illustrates how the two strands of the parental dna molecule separate, and how each strand functions as a template for synthesis of a new.
DNA Replication Microbiology
Ribonucleic acid (rna) is a molecule that is present in the majority of living organisms and viruses. In the laboratory setting, pfu is used to amplify dna in the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), where the enzyme serves the central function of copying a new strand of dna during each extension step. The semiconservative model of dna replication illustrates how the two strands of the parental dna molecule separate, and how each strand functions as a template for synthesis of a new.
The Structure of DNA
Uracil (/ ˈ j ʊər ə s ɪ l /) (symbol u or ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid rna.the others are adenine (a), cytosine (c), and guanine (g). It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups. The semiconservative model of dna replication illustrates how the two strands of the parental dna molecule separate, and how each strand functions as a template for synthesis of a new.
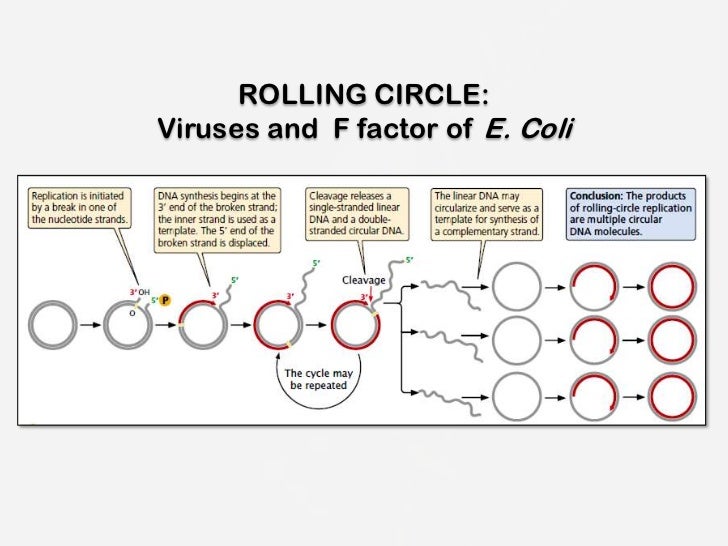
Replication
In the laboratory setting, pfu is used to amplify dna in the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), where the enzyme serves the central function of copying a new strand of dna during each extension step. Uracil (/ ˈ j ʊər ə s ɪ l /) (symbol u or ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid rna.the others are adenine (a), cytosine (c), and guanine (g). It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups.
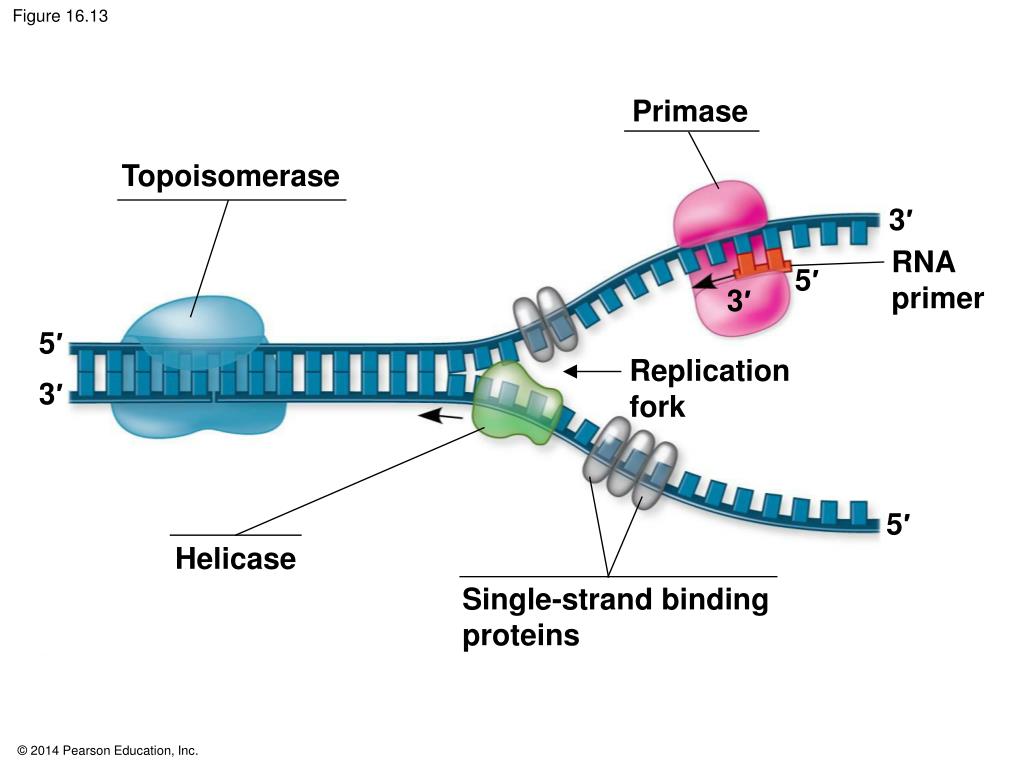
A Small Helical Bundle Prepares Primer Synthesis by Binding Two
Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. Pfu dna polymerase is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon pyrococcus furiosus, where it functions to copy the organism's dna during cell division. Uracil (/ ˈ j ʊər ə s ɪ l /) (symbol u or ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid rna.the others are adenine (a), cytosine (c), and guanine (g).
PPT The Molecular Basis of Inheritance PowerPoint Presentation ID
Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Ribonucleic acid (rna) is a molecule that is present in the majority of living organisms and viruses.
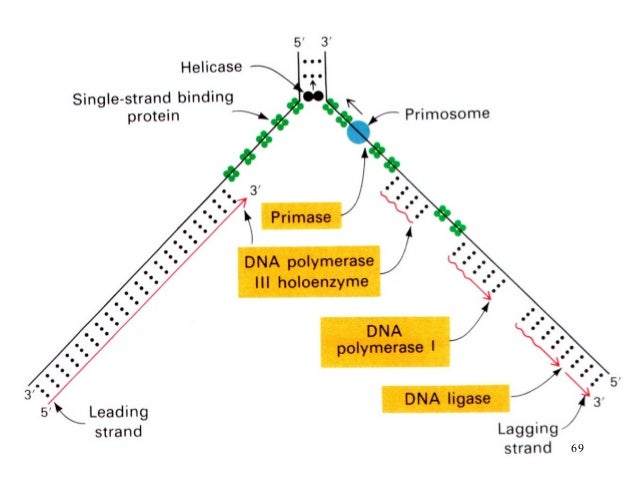
DNA Replication in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
The semiconservative model of dna replication illustrates how the two strands of the parental dna molecule separate, and how each strand functions as a template for synthesis of a new. It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups. The nitrogenous bases include adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.
Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. Uracil (/ ˈ j ʊər ə s ɪ l /) (symbol u or ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid rna.the others are adenine (a), cytosine (c), and guanine (g). It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups. The nitrogenous bases include adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. Ribonucleic acid (rna) is a molecule that is present in the majority of living organisms and viruses. Pfu dna polymerase is an enzyme found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon pyrococcus furiosus, where it functions to copy the organism's dna during cell division. In the laboratory setting, pfu is used to amplify dna in the polymerase chain reaction (pcr), where the enzyme serves the central function of copying a new strand of dna during each extension step. The semiconservative model of dna replication illustrates how the two strands of the parental dna molecule separate, and how each strand functions as a template for synthesis of a new. Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine.
In rna, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds.in dna, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (t).