Dna Template Definition
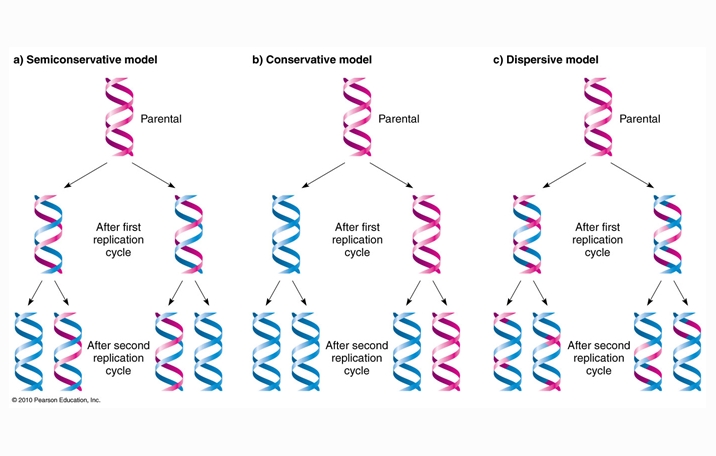
Dna template definition - The configuration of the dna molecule is highly stable, allowing it to act as a template for the replication of new dna molecules, as well as for the production (transcription) of the related rna (ribonucleic acid) molecule.a segment of dna that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a specific protein is called a gene. Fortunately, much of the damage done to dna by spontaneous chemical reactions in the nucleus, chemical. However, dna replication is catalyzed by a set of enzymes. The parental strands will act as a template for newly synthesising daughter strands. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the. Dna replicates by separating into two single strands,. Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity. Dna polymerase 1 is a dna polymerase encoded by the pola gene and is involved in the.
The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna. It is a unique and complex process that takes place in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
DNA Definition, Structure, Function and Replication Science Shape
The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. It is a unique and complex process that takes place in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Fortunately, much of the damage done to dna by spontaneous chemical reactions in the nucleus, chemical.
X chromosome may control male fertility Literacy Project
The configuration of the dna molecule is highly stable, allowing it to act as a template for the replication of new dna molecules, as well as for the production (transcription) of the related rna (ribonucleic acid) molecule.a segment of dna that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a specific protein is called a gene. Dna polymerase 1 is a dna polymerase encoded by the pola gene and is involved in the. However, dna replication is catalyzed by a set of enzymes.
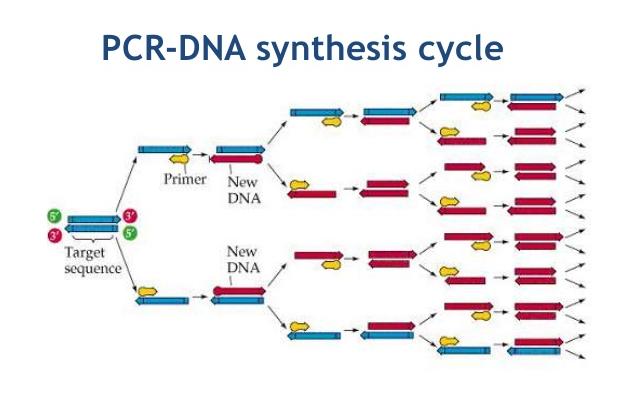
DNA Synthesis Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Definition, Procedure
Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3. Fortunately, much of the damage done to dna by spontaneous chemical reactions in the nucleus, chemical. Dna polymerase 1 is a dna polymerase encoded by the pola gene and is involved in the.
What Is the Connection between Anemia and Hematocrit Levels?
Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna. The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. Dna replicates by separating into two single strands,.
Sense and antisense strands of DNA YouTube
Fortunately, much of the damage done to dna by spontaneous chemical reactions in the nucleus, chemical. Dna polymerase 1 is a dna polymerase encoded by the pola gene and is involved in the. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand.
Three Things I Learned About DNA at WDYTYA Live
It is a unique and complex process that takes place in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, dna replication is catalyzed by a set of enzymes. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna.
RNA integrity and quantification
Dna polymerase 1 is a dna polymerase encoded by the pola gene and is involved in the. The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the.
Biochem dna technology(29.6.10)
The parental strands will act as a template for newly synthesising daughter strands. It is a unique and complex process that takes place in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3.
Dna replicates by separating into two single strands,. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. The parental strands will act as a template for newly synthesising daughter strands. The enzyme aids the base pairing of incoming nucleotides with the template strand. The configuration of the dna molecule is highly stable, allowing it to act as a template for the replication of new dna molecules, as well as for the production (transcription) of the related rna (ribonucleic acid) molecule.a segment of dna that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a specific protein is called a gene. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the. However, dna replication is catalyzed by a set of enzymes. Fortunately, much of the damage done to dna by spontaneous chemical reactions in the nucleus, chemical. Dna polymerase 3 possess 3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity.
The other function of dna polymerase 3 is proofreading the replicated dna. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna. Dna polymerase 1 is a dna polymerase encoded by the pola gene and is involved in the. It is a unique and complex process that takes place in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.