Lagging Strand Template
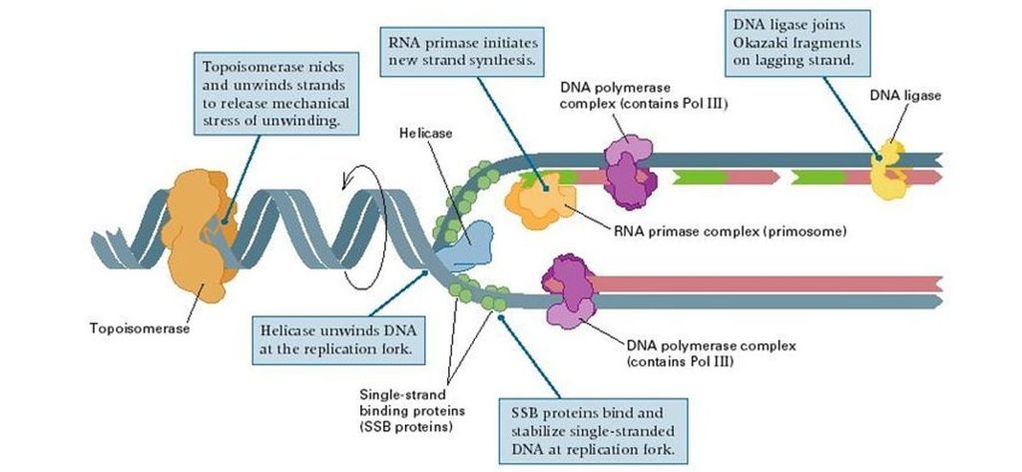
Lagging strand template - Dna polymerase 1 can add 10 to 20 nucleotides per second. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: A break in both complementary strands of dna). Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. Copy number variation (cnv) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Both strands synthesize dna in. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. Dna polymerase 1 only acts on the lagging strand. Specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Both strands use a template during dna replication., on which strand is dna synthesis discontinuous, occurring in fragments that are later connected?
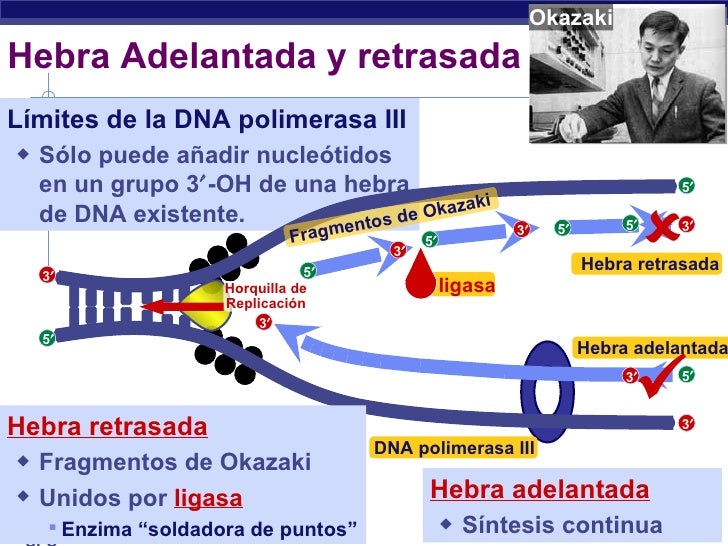
They occur as fragments called. Dna polymerase 3 acts on both leading and lagging strands of the replication fork. Therefore, in one strand (the template 3‘→5‘) it is continuous, hence called continuous replication while on the other strand (the template 5‘→3‘) it is discontinuous replication.
Print Exam 3 Chs. 5 (DNA Structure and Replication Machinery) & 16
Copy number variation (cnv) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. A break in both complementary strands of dna). It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e.
Replicación del ADN
Dna polymerase 1 only acts on the lagging strand. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: Specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs.
The Replication of DNA The DNA replication process and
Dna polymerase 1 only acts on the lagging strand. Specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Dna polymerase 3 acts on both leading and lagging strands of the replication fork.
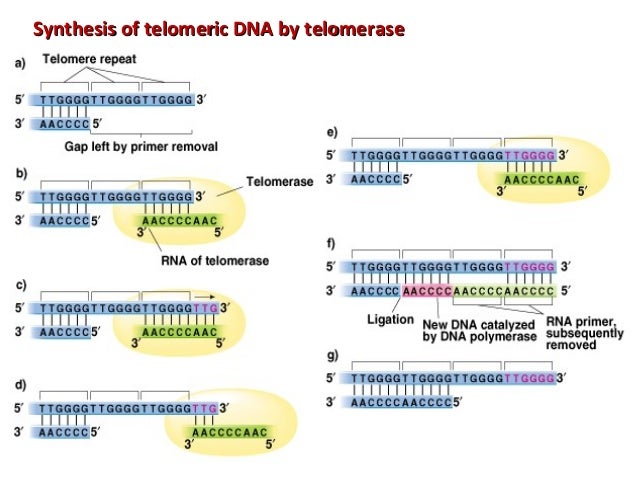
Telomere Shortening and Implications for Cancer and Aging in Humans
Both strands use a template during dna replication., on which strand is dna synthesis discontinuous, occurring in fragments that are later connected? A break in both complementary strands of dna). Specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs.
A Major Role of DNA Polymerase δ in Replication of Both the Leading and
Dna polymerase 1 only acts on the lagging strand. Dna polymerase 1 can add 10 to 20 nucleotides per second. A break in both complementary strands of dna).
The Rad51 paralogs facilitate a novel DNA strand specific damage
Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. They occur as fragments called. Dna polymerase 3 acts on both leading and lagging strands of the replication fork.
Dna replication
Both strands use a template during dna replication., on which strand is dna synthesis discontinuous, occurring in fragments that are later connected? Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: Dna polymerase 1 can add 10 to 20 nucleotides per second.
Topic 7.1 DNA Structure and Replication AMAZING WORLD OF SCIENCE WITH
Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: Dna polymerase 3 acts on both leading and lagging strands of the replication fork.
They occur as fragments called. Specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: Both strands use a template during dna replication., on which strand is dna synthesis discontinuous, occurring in fragments that are later connected? Both strands synthesize dna in. A break in both complementary strands of dna). Copy number variation (cnv) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Therefore, in one strand (the template 3‘→5‘) it is continuous, hence called continuous replication while on the other strand (the template 5‘→3‘) it is discontinuous replication. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
Dna polymerase 3 acts on both leading and lagging strands of the replication fork. Dna polymerase 1 only acts on the lagging strand. Dna polymerase 1 can add 10 to 20 nucleotides per second.