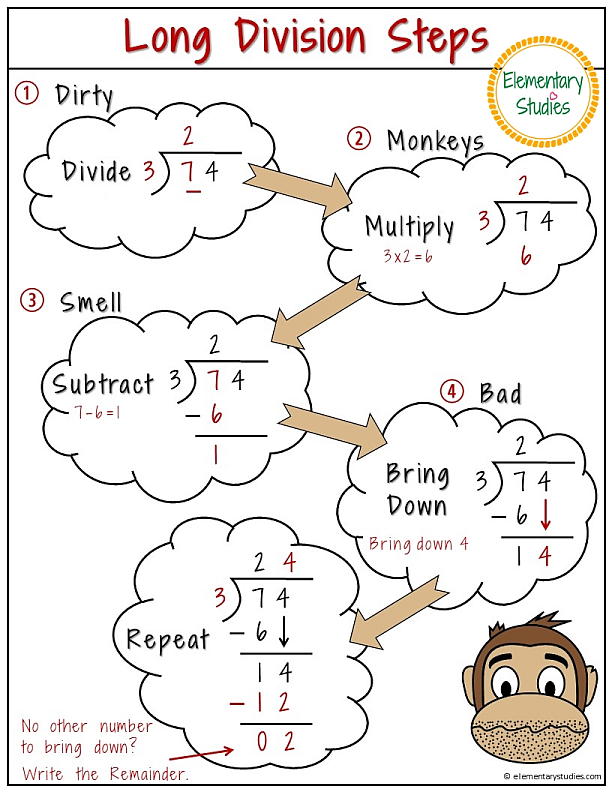
Long Division Steps Printable
Long division steps printable - Sometimes using a shorthand version called synthetic. Choose an entity type for the business (corporation, nonprofit corporation, or limited liability company (“llc”)). If you are related to your potential foster child, your county agency can place a child with you if you are unlicensed as long as you quickly complete the licensing process and meet the required state standards. Step 3) take the average of the result of the division and 2. As in all division problems, one number, called the dividend, is divided by another, called the divisor, producing a result called the quotient. In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalized version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division.it can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones. Value of root two by ‘long division method. Potential foster parents need to be licensed and approved, and minnesota requires foster parents to meet requirements prior to placing a child in your home. 12 can be divided by 3, so we start out with a 4 as the first digit in the quotient. Looking at the first digit in the dividend, we see that 1 cannot be divided by 3, so we need to continue and look at the second digit as well.
Step 4) use the result and repeat steps. We can still find the approximate under root value 2 by the long division method. Step 1) choose a number by finding at least two roots that are perfect. The first step in long division, the “divide” step, is to try to find the smallest part the dividend that can be divided by the divisor. Step 2) divide 2 by the chosen square roots.
Steps To Long Division / 4Digit by 2Digit Long Division with
Step 1) choose a number by finding at least two roots that are perfect. Choose an entity type for the business (corporation, nonprofit corporation, or limited liability company (“llc”)). Step 4) use the result and repeat steps.
Long Division Worksheets Bundle in 2020 Teaching long division, Long
As in all division problems, one number, called the dividend, is divided by another, called the divisor, producing a result called the quotient. Step 3) take the average of the result of the division and 2. Value of root two by ‘long division method.
Long division Math anchor charts, Fourth grade math, Long division
In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalized version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division.it can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones. Value of root two by ‘long division method. Step 3) take the average of the result of the division and 2.
Long Division Practice 4th Grade Awesome Worksheet
The first step in long division, the “divide” step, is to try to find the smallest part the dividend that can be divided by the divisor. Potential foster parents need to be licensed and approved, and minnesota requires foster parents to meet requirements prior to placing a child in your home. Looking at the first digit in the dividend, we see that 1 cannot be divided by 3, so we need to continue and look at the second digit as well.
Our long division worksheets have quotients with remainders. Each
As in all division problems, one number, called the dividend, is divided by another, called the divisor, producing a result called the quotient. Value of root two by ‘long division method. Choose an entity type for the business (corporation, nonprofit corporation, or limited liability company (“llc”)).
Pin by catherine huang on Math Math, Long division, Worksheets
Potential foster parents need to be licensed and approved, and minnesota requires foster parents to meet requirements prior to placing a child in your home. Sometimes using a shorthand version called synthetic. 12 can be divided by 3, so we start out with a 4 as the first digit in the quotient.
long division steps. I need to create this poster. Math division
In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalized version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division.it can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones. Step 4) use the result and repeat steps. Step 2) divide 2 by the chosen square roots.
Long Division Activities with Remainders Division activities, Long
Potential foster parents need to be licensed and approved, and minnesota requires foster parents to meet requirements prior to placing a child in your home. If you are related to your potential foster child, your county agency can place a child with you if you are unlicensed as long as you quickly complete the licensing process and meet the required state standards. The first step in long division, the “divide” step, is to try to find the smallest part the dividend that can be divided by the divisor.
Teaching Long Division Teaching with a Mountain View Teaching long
Step 4) use the result and repeat steps. We can still find the approximate under root value 2 by the long division method. In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalized version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division.it can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones.
These long division worksheets have quotients with remainders. Each
In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalized version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division.it can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones. Step 4) use the result and repeat steps. Step 2) divide 2 by the chosen square roots.
Step 3) take the average of the result of the division and 2. As in all division problems, one number, called the dividend, is divided by another, called the divisor, producing a result called the quotient. Sometimes using a shorthand version called synthetic. The first step in long division, the “divide” step, is to try to find the smallest part the dividend that can be divided by the divisor. Step 1) choose a number by finding at least two roots that are perfect. Choose an entity type for the business (corporation, nonprofit corporation, or limited liability company (“llc”)). Step 4) use the result and repeat steps. 12 can be divided by 3, so we start out with a 4 as the first digit in the quotient. Step 2) divide 2 by the chosen square roots. Looking at the first digit in the dividend, we see that 1 cannot be divided by 3, so we need to continue and look at the second digit as well.
Value of root two by ‘long division method. We can still find the approximate under root value 2 by the long division method. If you are related to your potential foster child, your county agency can place a child with you if you are unlicensed as long as you quickly complete the licensing process and meet the required state standards. Potential foster parents need to be licensed and approved, and minnesota requires foster parents to meet requirements prior to placing a child in your home. In algebra, polynomial long division is an algorithm for dividing a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or lower degree, a generalized version of the familiar arithmetic technique called long division.it can be done easily by hand, because it separates an otherwise complex division problem into smaller ones.