Template Strand Definition
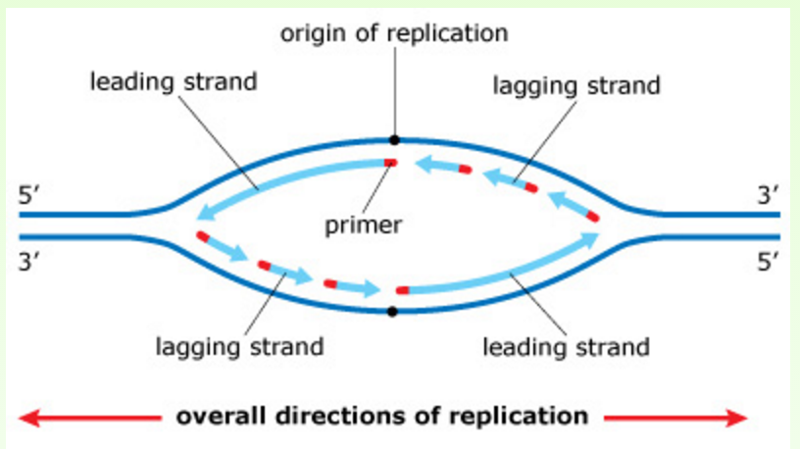
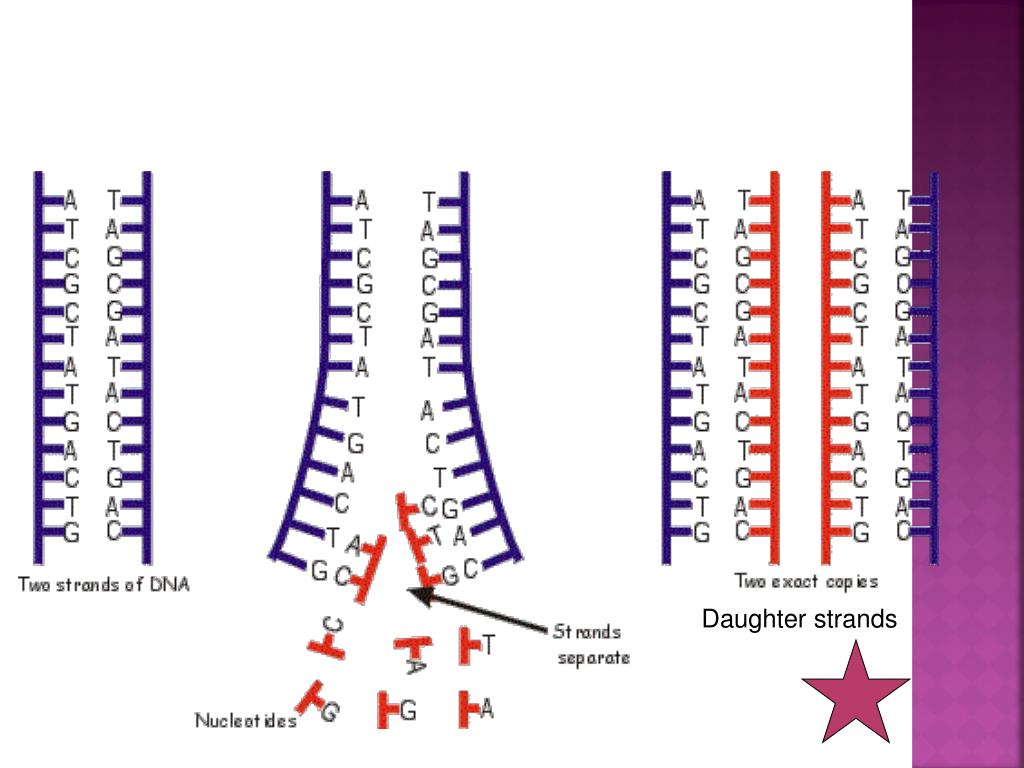
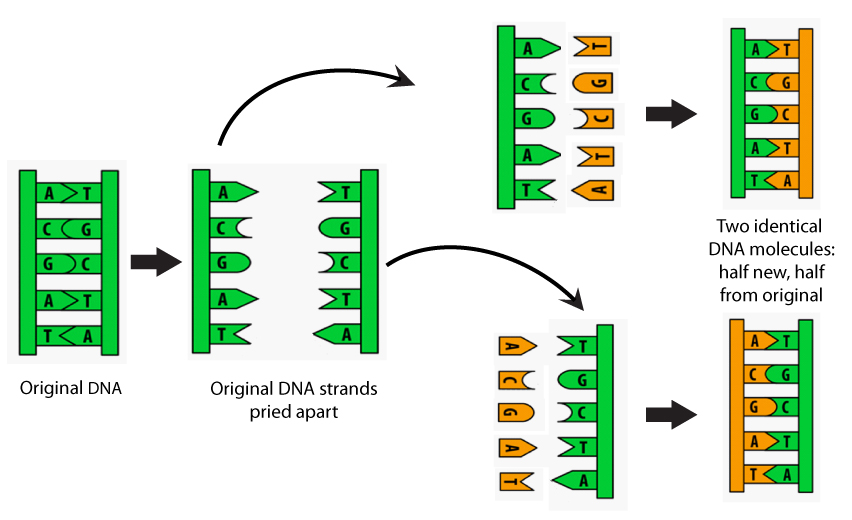
Template strand definition - It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. The replication process relies on the fact that each strand of dna can serve as a template for duplication. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome. In transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. Dna replication initiates at specific points, called origins, where the dna double helix. The antisense strand then becomes a template for making messenger rna, and the. Therefore, in one strand (the template 3‘→5‘) it is continuous, hence called continuous replication while on the other strand (the template 5‘→3‘) it is discontinuous replication.
They occur as fragments called. During protein productions, the two dna strands temporarily separate. The repair system makes this distinction by identifying the template strand. Radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna.
Lagging Strand of DNA Definition & Synthesis Video & Lesson
The repair system makes this distinction by identifying the template strand. The antisense strand then becomes a template for making messenger rna, and the. Dna replication initiates at specific points, called origins, where the dna double helix.
Translesion DNA Synthesis
Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. The repair system makes this distinction by identifying the template strand. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e.
Print Exam 3 Chs. 5 (DNA Structure and Replication Machinery) & 16
Radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna. The antisense strand then becomes a template for making messenger rna, and the. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.
Models of DNA replication, notes with Definition & diagram/
In transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. They occur as fragments called. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein.
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4688998
Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.
DNA III Biology Visionlearning
It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. During protein productions, the two dna strands temporarily separate. Dna replication initiates at specific points, called origins, where the dna double helix.
ADN III Biology Visionlearning
During protein productions, the two dna strands temporarily separate. Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
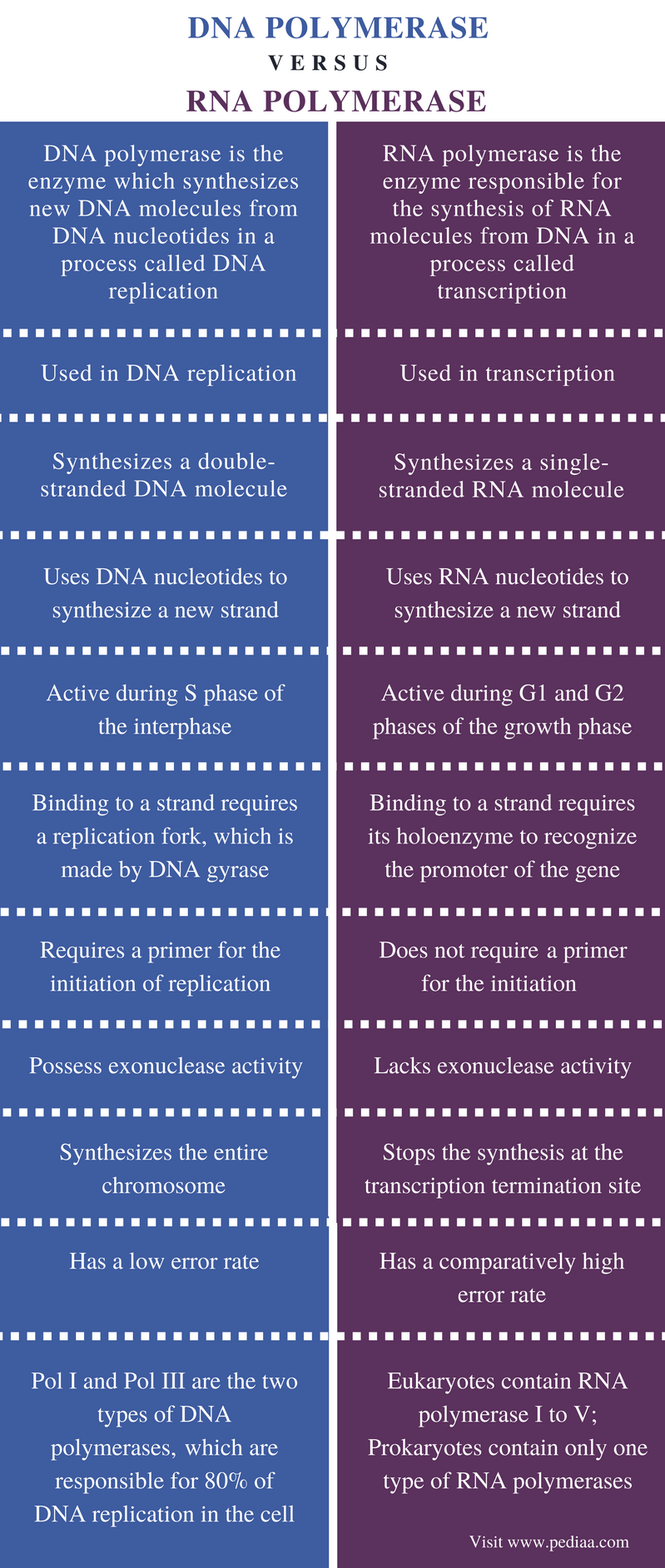
Difference Between DNA and RNA Polymerase Definition, Replication
In transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome.
The replication process relies on the fact that each strand of dna can serve as a template for duplication. Dna is always polymerised only in the 5′ to 3′ direction. Dna replication initiates at specific points, called origins, where the dna double helix. They occur as fragments called. During protein productions, the two dna strands temporarily separate. The antisense strand then becomes a template for making messenger rna, and the. The repair system makes this distinction by identifying the template strand. Dna repair is a collection of cellular responses by which a cell identifies and corrects any damage to the dna molecules that encode its genome. Therefore, in one strand (the template 3‘→5‘) it is continuous, hence called continuous replication while on the other strand (the template 5‘→3‘) it is discontinuous replication. It is to be noted that elongation is unidirectional i.e.
In transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. Radiation, chemical mutagens, heat, enzymatic errors, and spontaneous decay constantly damage dna. Template definition, a pattern, mold, or the like, usually consisting of a thin plate of wood or metal, serving as a gauge or guide in mechanical work. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein.